Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- admin
- Uncategorized
The Impact of Regenerative Drugs in the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Abstract:
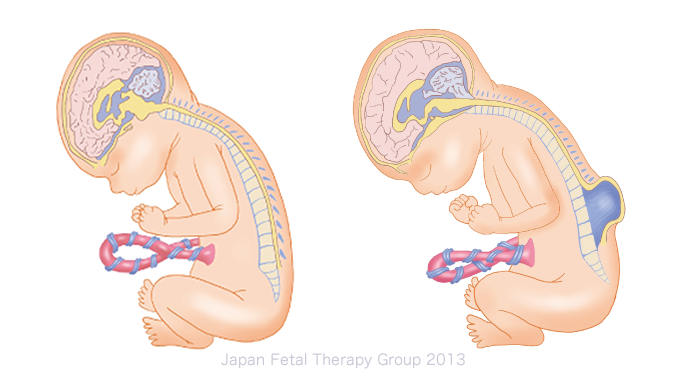
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system that leads to the degradation of the myelin sheath surrounding nerve fibers. This demyelination disrupts neural communication and results in symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, balance issues, and visual and cognitive disturbances. Regenerative drugs, by promoting myelin repair, enhancing neuronal function, and improving the overall health of the nervous system, play a significant role in the effective management and treatment of MS.
Introduction:
In MS, the immune system mistakenly attacks the myelin sheath in the brain and spinal cord. This leads to demyelinated areas that impair normal neuron function. While conventional treatments can slow disease progression, regenerative therapies offer the potential to restore damaged neural structures and recover some degree of sensory and motor function.
Mechanism of Action of Regenerative Drugs:
Regenerative drugs work by stimulating oligodendrocytes—the cells responsible for myelin production—to regenerate the damaged myelin around neurons. These drugs also create a favorable environment for neural repair by:
Reducing neuroinflammation
Enhancing mitochondrial function
Lowering oxidative stress
Increasing neuroplasticity and synaptic connectivity
Clinical Benefits of Regenerative Drugs:
Improved Neural Signal Transmission:
Patients treated with regenerative drugs have shown significant improvements in the speed and quality of neural signal transmission, particularly in motor and visual pathways.Enhanced Motor and Muscular Function:
These therapies help improve limb control, reduce muscle weakness and tremors, and restore mobility.Reduced Fatigue and Improved Daily Function:
Regular use of regenerative drugs has led to increased energy levels, decreased chronic fatigue, and an overall enhancement in quality of life.Cognitive and Mental Function Improvement:
Patients have reported better memory, focus, and mood stabilization as a result of improved brain function.Notable Changes in MRI Imaging:
Periodic MRI scans in many patients under regenerative treatment have revealed a reduction in brain lesions and signs of neural tissue repair.
Conclusion:
Regenerative drugs have marked a turning point in the treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. These medications not only help manage symptoms but also actively contribute to the repair of damaged myelin. Their use has led to improvements in motor, cognitive, and neurological functions, offering renewed hope for regaining lost abilities in MS patients.