Regenerative Medications
- admin
- Uncategorized
Regenerative Drugs: A New Era in the Treatment of Neuromuscular Disorders
Abstract:
Regenerative drugs represent one of the most advanced achievements in modern medicine, bringing about a major shift in the treatment of conditions that were previously considered untreatable or unmanageable. Designed to activate the body’s natural ability to repair tissues—especially neural and muscular tissues—these drugs offer new hope for patients with spinal cord injuries, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, ALS, and even conditions like incontinence. They provide the potential for restoring bodily functions and improving quality of life.
What Are Regenerative Drugs?
Regenerative drugs are a class of therapeutics primarily aimed at stimulating the repair of damaged tissues, enhancing neural connectivity, and boosting the body’s cellular activity. Unlike traditional drugs that mainly alleviate symptoms, regenerative drugs target the root of the disease, initiating natural healing and recovery processes.
Mechanisms of Action:
Activating the body’s stem cells to regenerate damaged tissues
Enhancing neural activity and restoring disrupted pathways between the brain and limbs
Reducing chronic inflammation and cellular damage in neural or muscular tissues
Stimulating the production of growth factors that support tissue repair
Modulating the immune system to prevent further tissue degeneration
Clinical Applications of Regenerative Drugs:
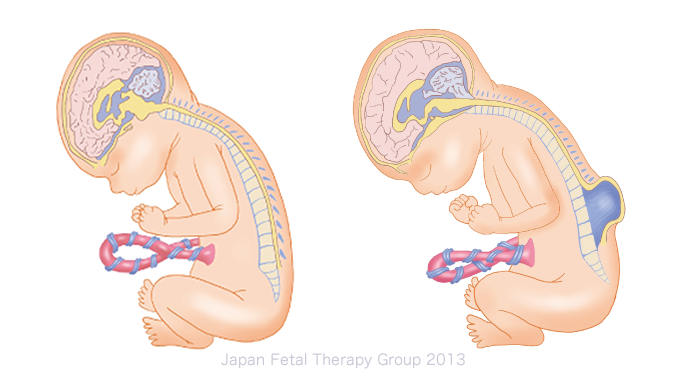
Spinal Cord Injuries (SCI):
Restoring sensory and motor function, reducing spasms, and regaining control over bladder and bowel movementsCerebral Palsy (CP):
Improving muscle tone, motor control, reducing spasticity, and enhancing speech developmentMultiple Sclerosis (MS):
Reducing relapse frequency, improving balance, decreasing fatigue, and strengthening limb movementParkinson’s Disease:
Reducing tremors, improving body control, decreasing muscle stiffness, and boosting cognitive capacityAmyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS):
Slowing disease progression, strengthening respiratory and motor muscles, and enhancing quality of lifeUrinary and Fecal Incontinence:
Repairing damaged neural pathways to the bladder and bowel, gradually restoring controlMuscular Atrophy:
Stimulating muscle growth, preventing further wasting, and regaining mobility
Key Advantages of Regenerative Drugs:
No need for high-risk or invasive surgeries
Compatible with physiotherapy and rehabilitation for enhanced effectiveness
Gradual but lasting improvements in motor and sensory function
Renewed hope and motivation for patients with chronic or disabling conditions
Conclusion:
Regenerative drugs demonstrate that in modern medicine, no path is a dead end. They offer a new hope for regaining lost functions, reducing dependency, and improving quality of life. With continued research, broader clinical use, and integration with other therapies, a brighter future awaits millions of patients around the world.